 |
Tokyo (AFP) Oct 12, 2007 Japanese researchers say they have found a way to let people stroll through the virtual world of Second Life using their own imagination, in a development that could help paralysis patients. Previous studies have shown people can move computer cursors through brain waves, but the Japanese team says it is the first to apply the technology to an Internet virtual world. The technology "would enable people suffering paralysis to communicate with others or do business through chatting and shopping in a virtual world," said Junichi Ushiba, associate professor at Keio Univesity's rehabilitation centre. Second Life is an increasingly popular virtual world in which people -- and animals -- are represented by animated avatars and can do everything from social activities to shopping. Ushiba said Second Life could motivate patients with severe paralysis, who are often too depressed to undergo rehabilitation. "If they can see with their own eyes their characters moving around, it could reinvigorate their brain activity and restore some functions," he said. Under the technology, a person wearing head gear embedded with electrodes, which analyse brain waves in the cerebral motor cortex, would be able to move a Second Life character forward by thinking he or she is walking. Imagining movement with the right or left hand would make the character turn accordingly in the same direction. Researchers have previously put similar technology to work to scan brain waves to control objects such as computer cursors and electrical gears. In the Keio University laboratory, the team has designed artificial arms that operate by reading brain waves, although none is known to be commercially available yet. Ushiba said the technology could help people undergoing neuro-rehabilitation by stimulating brain activity. Traditionally, "if a stroke leaves a man's right hand paralysed, he has been encouraged to use his left hand instead," Ushiba said. "More recently, however, it has come to light that the paralysed hand would start moving better if you try to use it," Ushiba said, noting that attempts to use a numb hand increase brain activity. The team next plans to test the technology on actual paralysis patients to see how they respond to the virtual world. Related Links Space Technology News - Applications and Research
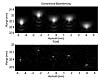 Charlottesville, VA (SPX) Jul 18, 2007
Charlottesville, VA (SPX) Jul 18, 2007University of Virginia Engineering School Associate Professor William F. Walker and Research Associate Francesco Viola have developed a new tool - an advanced imaging algorithm - that is, quite literally, transforming the way we see things. Together with graduate student Michael A. Ellis, biomedical engineering team has created an innovative method of signal processing that can be used with a broad range of imaging and sensing systems including ultrasound, RADAR, SONAR, telecommunications, and even a few optical imaging systems. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright Space.TV Corporation. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space.TV Corp on any Web page published or hosted by Space.TV Corp. Privacy Statement |