 |
Pasadena, CA (SPX) May 10, 2010 The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument on NASA's Terra spacecraft captured this nighttime image of the growing oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico on May 7, 2010. On April 20, an explosion destroyed the Deepwater Horizon oil platform operating in the Gulf 80 kilometers (50 miles) offshore, resulting in substantial loss of life and releasing 5,000 barrels of oil per day into the water. The huge oil slick was being carried towards the Mississippi River Delta, and small amounts of oil had reached the Louisiana, Alabama and Mississippi shores by May 3. This thermal image from ASTER covers an area measuring 60 by 240 kilometers (37 by 147 miles), most of it over the Gulf of Mexico. The coldest surfaces appear dark, and the warmest appear white. The city of Pascagoula, Miss., is visible in the upper right corner; at night the land is colder (darker) than the Gulf waters. Offshore islands below Pascagoula also appear dark compared to the surrounding ocean. The black dots and patches over the Gulf waters are small clouds, particularly in the southern half of the image. The thickest parts of the oil spill appear as dark grey, filamentous masses in the southern part of the image, extending off the bottom. Other dark-light swirl patterns are water currents where different temperature water masses are visible.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links the missing link Earth Observation News - Suppiliers, Technology and Application
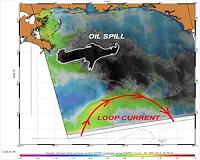 Envisat Monitors Oil Spill Proximity To Loop Current
Envisat Monitors Oil Spill Proximity To Loop CurrentParis, France (ESA) May 06, 2010 As fears grow that the Loop Current in the Gulf of Mexico could soon catch the oil slick and drag it south towards coral reefs in the Florida Keys, scientists are monitoring the situation closely with ESA's Envisat radar data. By combining surface roughness and current flow information with Envisat Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (ASAR) data of the spill, SAR image analysts are able to d ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |